## Understanding Pitbull Behavior: Deciphering Signs and Signals
Pitbulls, often perceived as aggressive dogs, possess intricate behaviors that require careful interpretation. This article delves into the subtle body language cues, vocalizations, and social interactions that can help you understand what your Pitbull is communicating.
By dissecting tail wagging, ear postures, and eye contact, we uncover the nuances of their body language. Vocalizations, such as growling, barking, and whining, provide further insights into their emotional state. We explore how social interactions with humans and other animals shape their behavior.
Environmental factors, including socialization and training, play a significant role in molding a Pitbull’s temperament. While breed variations and individual characteristics must be considered, responsible ownership practices and an understanding of their innate traits are crucial for fostering a harmonious relationship with these misunderstood canines.
**Subheading 1: Body Language Cues**
Tail Wagging:
* **Slow, relaxed wag:** Contentment, friendliness
* **Fast, energetic wag:** Excitement, playfulness
* **Low, tucked tail:** Fear, submission
Ears:
* **Pricked up:** Alertness, curiosity
* **Folded back:** Fear, aggression
* **Partially folded back:** Uncertainty, anxiety
Eyes:
* **Relaxed, almond-shaped:** Contentment, calmness
* **Hard, narrowed:** Aggression, hostility
* **Wide, dilated:** Fear, shock
**Subheading 2: Vocalizations**
Growling:
* **Low, rumbling:** Warning, aggression
* **High-pitched, sharp:** Fear, discomfort
* **Excited growl:** Playfulness, anticipation
Barking:
* **Short, sharp barks:** Alarm, attention-seeking
* **Long, continuous barks:** Territorial defense, distress
* **Yapping:** Excitement, anxiety
Whining:
* **Low, mournful cry:** Separation anxiety, pain
* **High-pitched, urgent:** Excitement, distress
**Subheading 3: Social Interactions**
Interactions with Humans:
* **Friendly tail wags, licking:** Affiliation, affection
* **Growling, lunging:** Aggression, fear
* **Cowering, avoiding eye contact:** Submission
Interactions with Other Animals:
* **Playful body language:** Bouncing, chasing
* **Aggressive body language:** Staring, growling
* **Avoidance:** Fear, discomfort
**Subheading 4: Environmental Factors**
Socialization:
* Positive socialization experiences reduce aggression and fear
* Lack of socialization can lead to reactivity and anxiety
Training:
* Obedience training improves communication and control
* Lack of training can result in unpredictable behavior
**Subheading 5: Additional Considerations**
Breed Variations:
* Pitbulls are a diverse breed with individual temperaments
* Some lines may be more prone to aggression than others
Individual Temperament:
* Each pitbull has a unique personality that influences behavior
* Genetics, environment, and life experiences all play a role
Responsible Ownership Practices:
* Spaying or neutering reduces aggression and roaming
* Exercise and mental stimulation promote well-being and reduce boredom
* Supervision and control in public areas ensure safety and prevent incidents
The #1 Free Source for Pitbull & Bully Pedigrees!
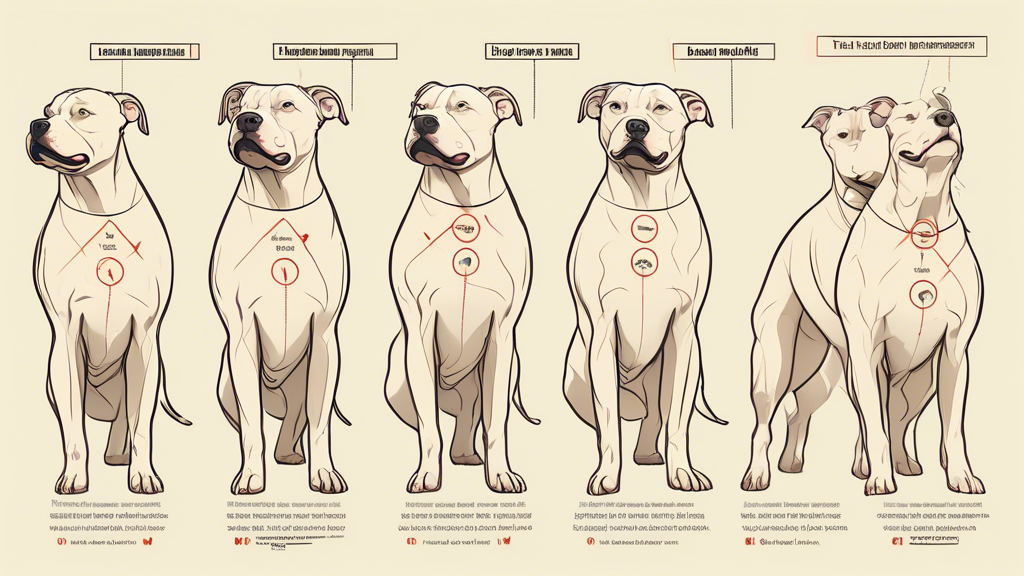
## Body Language Cues: Understanding Pitbull Signaling
Pitbull body language offers valuable insights into their emotional state and intentions. Several key cues can help you decipher their communication:
### Tail Wagging
Tail wagging can indicate various emotions in Pitbulls:
– **High, Wide Wag:** Generally a sign of happiness, excitement, or playfulness.
– **Low, Slow Wag:** May signal uncertainty, anxiety, or discomfort.
– **Tucked Tail:** A sign of fear, submission, or aggression.
### Ears
Ears play a crucial role in Pitbull communication:
– **Relaxed, Forward-Facing Ears:** Typically indicate alertness, curiosity, or interest.
– **Pricked Ears:** Signal excitement, attention, or potential aggression.
– **Flattened Ears:** Convey fear, submission, or defensiveness.
### Eyes
Pitbull eyes can be expressive, so pay attention to their gaze:
– **Hard Stare:** Can indicate suspicion, aggression, or a dominance challenge.
– **Soft Gaze:** Often conveys relaxation, contentment, or trust.
– **Whale Eye:** When Pitbulls show the whites of their eyes, it can signal fear or potential aggression.
**Conclusion:**
Understanding pitbull behavior is crucial for responsible ownership and safe interactions. By recognizing their body language cues, vocalizations, and social interactions, we can effectively interpret their intentions and respond appropriately. Additionally, taking into account environmental factors, breed variations, and individual temperament further enhances our ability to establish harmonious relationships with these canine companions.
It is paramount to emphasize that all dogs, including pitbulls, possess the potential for aggression if they feel threatened or provoked. However, through proper socialization, consistent training, and a responsible approach to ownership, we can foster positive and well-adjusted pitbulls that contribute to a safe and enjoyable environment for both themselves and those around them.
Ultimately, the key to understanding pitbull behavior lies in respectful communication, attentive observation, and a genuine appreciation for the unique characteristics of each individual dog. By embracing these principles, we can cultivate strong bonds with these loyal and affectionate animals and ensure their well-being and happiness throughout their lives.













Leave A Comment